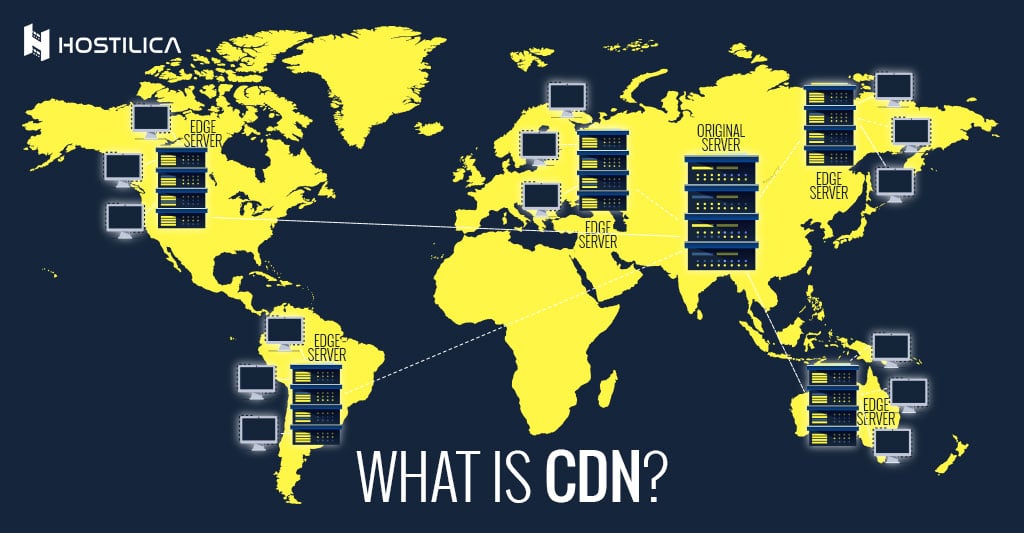
A Content Delivery Network is a vital component of any good-old-fashioned website and software these days. The content you see on your smartphones today, on almost any site or app, images or videos, or any other sort of online content will be delivered over a content delivery network. This means the internet is divided up into many different “neighborhoods” where the same content is made available across various networks – this makes it far easier for the end-user to find what they want, and the data doesn’t have to travel all over the world. They simply go to their PC, fire up the relevant software, enter their credit card details and it’s done. Simple!
In terms of the technology itself, a CDN works by using IPs or IP networks that are fast enough to be able to route packets of information much faster. The reason why many companies (not just those in telecommunication) are getting a CDN is that they have a common use case which is people accessing information from mobile devices, such as smartphones, tablets and laptops from different parts of the world. With a common use case such as this, there’s a much greater potential for traffic to increase on a CDN.
With a CDN technology system, every server connected to the system is essentially acting as an “edge server”. The edge servers act as “redundant” connections since all the data requests will be routed through the edge servers and not directly from the source servers. This means that with each request, your computer gets the request for that data in its pool and then sends that request out along to whichever edge servers it can find. This saves time since the user doesn’t have to wait for the actual source server to receive the request. This saves you lots of bandwidth, which is especially important if your website has a lot of traffic from different parts of the world.
The CDN provider also ensures that no packets are lost and that they arrive at their destinations promptly increasing the network’s reliability.
Conclusion
CDN allows for faster and higher quality transmission and reception of information because all of the information is handled internally. Because of these key components, CDN is becoming increasingly popular in many different circumstances, from enterprise to residential use and from large institutions to small ones.